Chemotaxis is a dynamic process of cell movement, which represents an important class of cell-cell communication through chemical signaling and plays crucial roles in many physiological and pathological processes. Besides the Boyden chamber assay which is common to study the cellular chemotaxis, microfluidic chamber assay has been gaining popularity for the macro-scale chemotaxis assays in real space and time with the disadvantages of generating a long-term stable and controllable gradient of soluble factors that can be continuously monitored over time. This technology gets the potential to create well defined spatial and temporal chemical concentration gradients and allows a true ongoing assessment of chemotaxis versus chemokinesis. Furthermore, with the utilization of high throughput screening in this technique, the study of chemotaxis in real time and at single cell level come true.
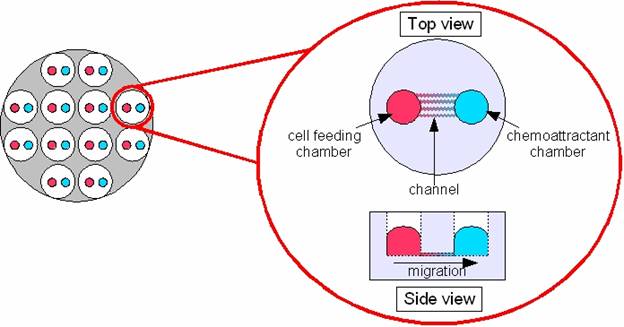 Figure 1. The schematic diagram of microfluidic chamber assay
Figure 1. The schematic diagram of microfluidic chamber assay
Microfluidics devices in this assay contain networks of micron-dimension channels, which enable integration of multiple processes on a single platform and reduce reagent consumption and analysis time. The device will have two chambers connected by an internal channel. Cells are seeded and adhere to the bottom on one side and stable, linear or nonlinear gradients are generated on the other side. Then, cell migration can be observed in real time and high resolution by high throughput screening. An obvious advantage of this technique is the similarity in dimensions of cells and microchannels, which can perform cell migration assays with the highest accurate and micro-scale. The small assay volumes make these assays well suitable for the studies with rare cell types and precious reagents. In addition, channels with this size are characterized by laminar flow and the combination of laminar flow and diffusion enables rapid and repeatable reagents delivery and highly resolved chemical gradients. Another distinct advantage of microfluidic devices is the increased surface-to-volume ratio which facilitates favorable scaling of heat and mass transfer and the assessment of directed chemotaixs along a gradient.
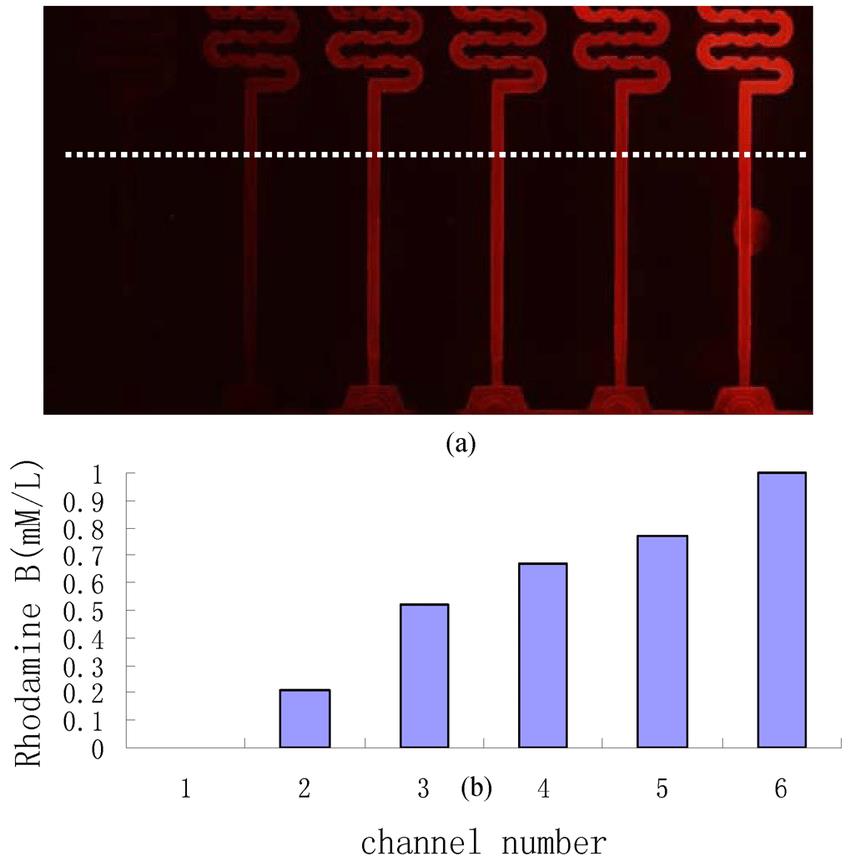 Figure 2. The experimental results of microfluidic chamber assay
Figure 2. The experimental results of microfluidic chamber assay
In our laboratory, microfluidic chemotaxis devices are designed with both physical and biological consideration, which offer more precise and consistent results. We can conduct the assay with rare cells and reagents, which is convenient and helpful, especially for studies on expensive drugs or rare primary cells. The high throughput screening system also allows for the prefect analysis for the results.

*If your organization requires signing of a confidentiality agreement, please contact us by email.
Online Inquiry