Scratch Assay, also known as the Wound Healing Assay, is a widely used in vitro technique to study cell migration and wound healing processes. This assay involves creating a "scratch" or gap in a monolayer of cultured cells and observing the migration of cells to fill the gap over time. It is commonly used to assess the migratory properties of cells and to study factors that influence cell migration, such as growth factors, drugs, or other treatments.
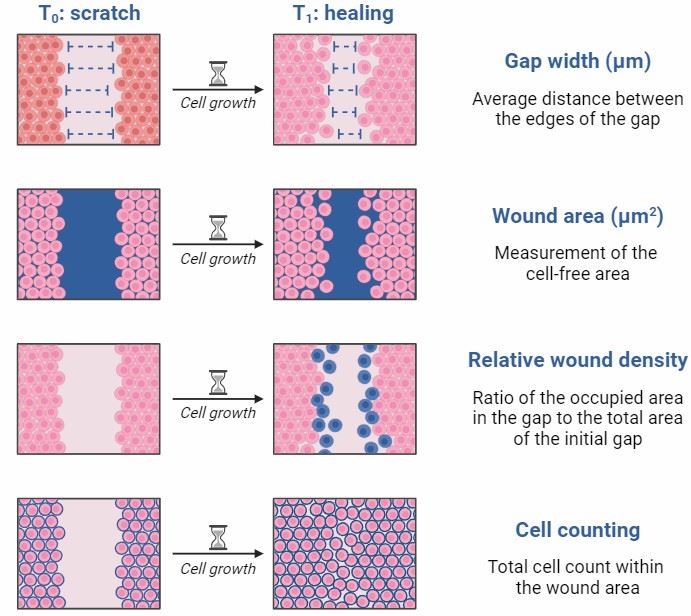 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of scratch (wound healing) assay.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of scratch (wound healing) assay.
Creative Bioarray provides a comprehensive suite of products and services to support the Scratch (Wound Healing) Assay. We offer a variety of cell lines and primary cells suitable for wound healing research, carefully selected to ensure optimal performance and reproducibility. Our high-quality cell culture reagents, including growth media and supplements, are specifically designed to promote cell health and viability during scratch assays.
Study Examples:
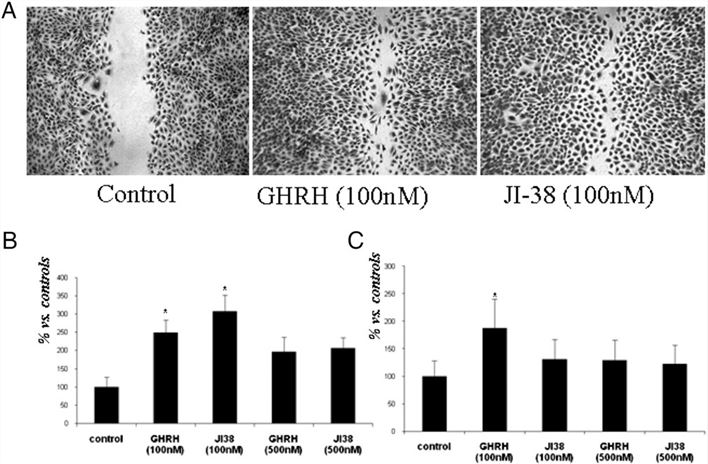 Figure 2. GHRH and JI-38 induce migration of cultured MEFs.[1]
Figure 2. GHRH and JI-38 induce migration of cultured MEFs.[1]
Reference:
1. Dioufa N, Schally AV, Chatzistamou I, et al. Acceleration of wound healing by growth hormone-releasing hormone and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(43):18611-18615. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013942107
Online Inquiry