Excitotoxicity, characterized by the excessive activation of excitatory neurotransmitters like glutamate, is widely recognized as a significant factor in the pathophysiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This process can lead to the dysfunction and eventual death of motor neurons, which is a key hallmark of the disease. Given its central role in ALS pathology, excitotoxicity is a target of interest for potential therapeutic interventions. Drugs that modulate glutamate signaling or target downstream pathways may hold promise for ALS treatment.
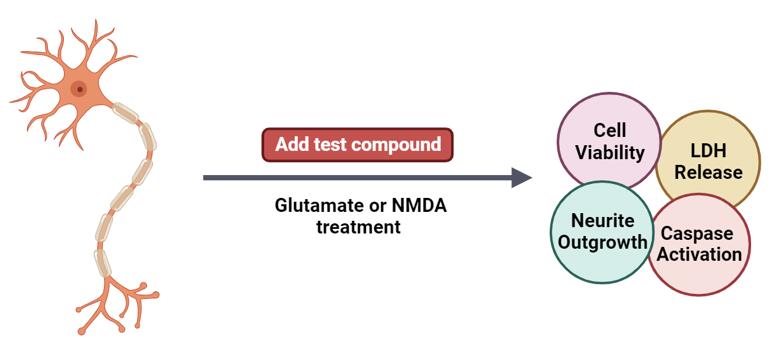
Creative Bioarray's in vitro excitotoxicity assay provides a swift assessment of a molecule's neuroprotective potential.
Online Inquiry