Gelatin degradation assay allows visualizing and quantifying invasion at the subcellular level instead of analyzing the invasive behavior of whole cells. This technique is of high resolution and can discover cellular protrusions called invadopodia and podosomes, which are protrusive structures in cancer cells and play an important role in cell attachment and remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM). These structures also contribute to the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells, thus the study of these cellular protrusions can lead to a valuable insight to the research of cell invasion. Gelatin degradation assay makes it possible to assess and quantify these cellular protrusions and is crucial in the study of cell invasion.
In the process of this assay, fluorophore-conjugated gelatin coated overslips are prepared and the gelatin coating is performed as homogeneous as possible. Thus, it is not good to coat too many coverslips at a time and repeat the process of coating coverslips as many times as necessary to obtain the desired final number of coverslips. Another important aspect of the process of preparing fluorescent gelatin-coated coverslips, this work should be reasonably completed quickly to avoid that the gelatin starts drying before it has formed a thin uniform coating of the coverslip. After the fluorescent gelatin-coated coverslips are prepared, transfer the desired number of coated coverslips to a new sterile 12-well plate. Cells are seeded on top of a thin layer of fluorescently labeled matrix and to record and measure regions where the cells degrade the matrix leaving behind areas that lack fluorescence. With the advanced high resolution living image system, sub-cellular high resolution data of invading structures can be made visible and these high valuable data can facilitate us to get a further understanding of the mechanisms of cell invasion.
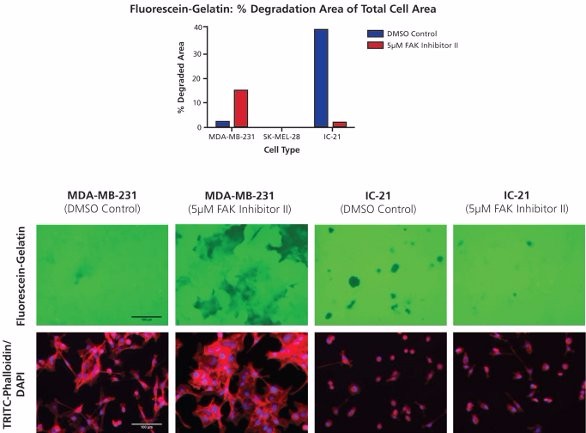
Gelatin degradation assay can be used in many studies including the research of podosome mediating macrophage invasion. It is also employed in the study of bioactive laminin-derived peptides increasing the activity of invadopodia. With more than 10 years of experience, experts at Creative Bioarray will optimize the experiment protocols to guarantee good results.

*If your organization requires signing of a confidentiality agreement, please contact us by email.
Online Inquiry