Ferroptosis is the term for a form of cell death that was recently coined in 2012. According to the study, ferroptosis is remarkably distinct from other types of cell death such as apoptosis, necroptosis, and autophagic cell death at morphological, biochemical, and genetic levels. Understanding the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of ferroptosis may provide new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to regulate cell survival and death in human disease. Creative Bioarray provides services for detecting ferroptosis-related Genes and protein expression to help your research on the molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis.
Iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation signaling are increasingly recognized as central mediators of ferroptosis. The activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway contributes to ferroptotic cancer cell death.
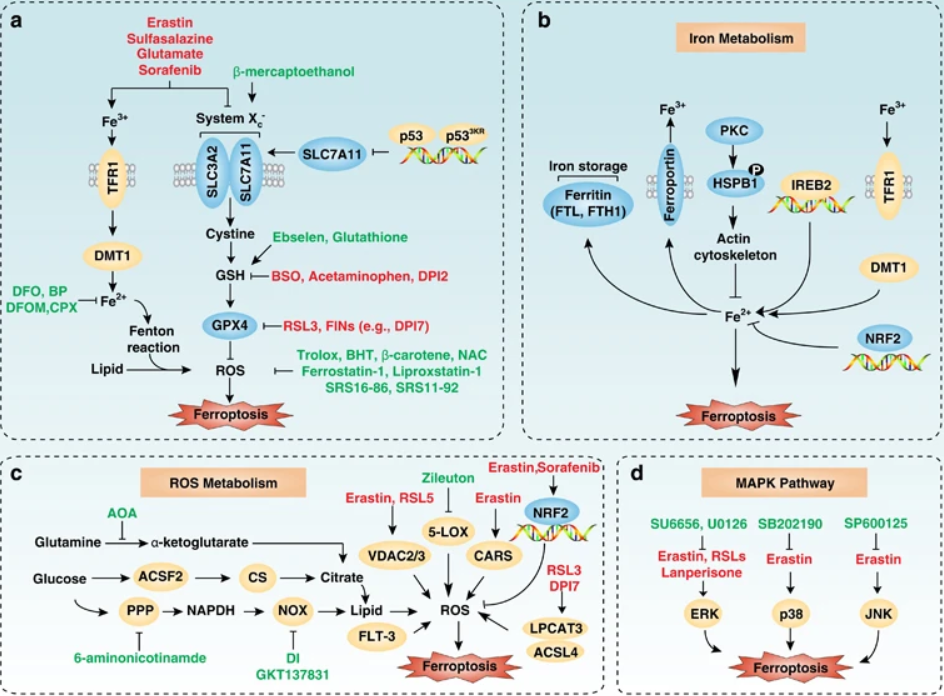 Figue 1. Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of ferroptosis. (a) Core regulators of ferroptosis. (b) Iron metabolism. (c) ROS metabolism (d) MAPK pathway. (Xie, et al. 2016)
Figue 1. Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of ferroptosis. (a) Core regulators of ferroptosis. (b) Iron metabolism. (c) ROS metabolism (d) MAPK pathway. (Xie, et al. 2016)
Ferroptosis is distinct from other forms of cell death at morphological, biochemical, and genetic levels. Our services include but are not limited to:
QPCR/WB Detection Service
Ferroptosis is tightly regulated by intracellular signaling pathways, including the regulatory pathway of iron homeostasis, the RAS/Raf/MAPK pathway and the cystine transport pathway. The intracellular Cox2, ACSL4, NOX1, GPX4, SLC7A11, Ferritin and Ferritin Light Chain and other related factors changed. Among them, Cox2, ACSL4 and NOX1 are up-regulated in ferroptosis cells. GPX4, SLC7A11, Ferritin and Ferritin Light Chain are down-regulated in ferroptosis cells.
Positive Regulators of Ferroptosis
Negative Regulators of Rerroptosis
The time depends on the experiment content
If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more detailed information.
References:
Online Inquiry