Macrophages are key components of the immune system, playing a crucial role in defending the body against infections and removing damaged or abnormal cells. One of the ways macrophages contribute to immune defense is through a process known as phagocytosis, where they engulf and digest foreign particles, microbes, or even unhealthy host cells. This process is part of the innate immune response.
Macrophages are found in all tissues and show great functional diversity, including the recognition and clearance of foreign, aged, and damaged cells. Activated macrophages can be used effectively as a cancer immunotherapy; they can kill cancer cells by themselves in a direct manner or indirectly through recruitment of other immune cells, such as cytotoxic T-lymphocytes.
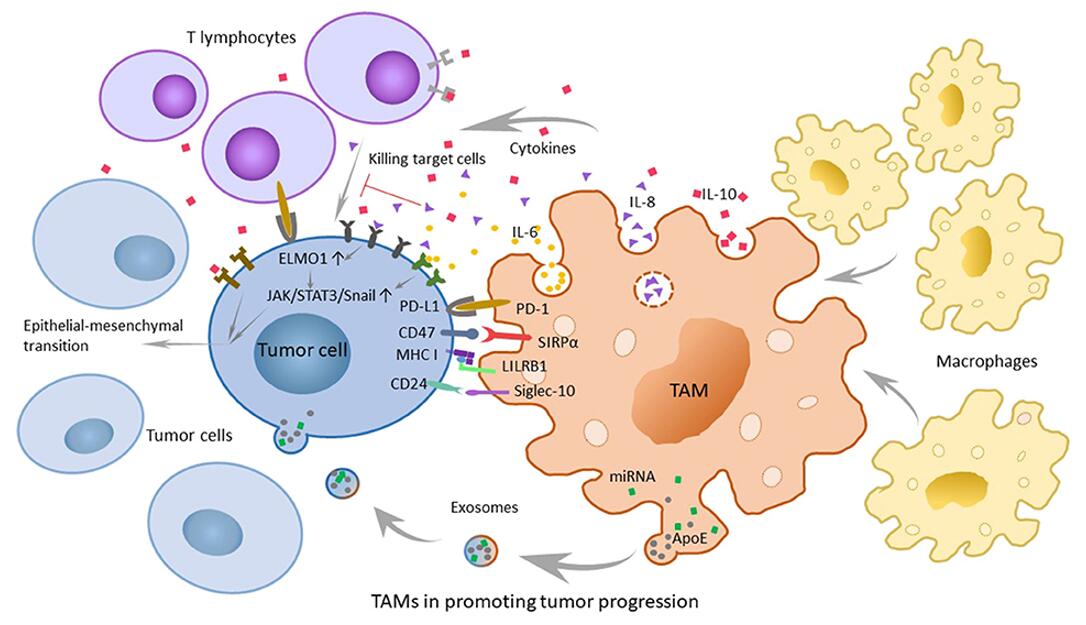 Figure 1. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in promoting tumor progression and related mechanisms. [1]
Figure 1. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in promoting tumor progression and related mechanisms. [1]
Macrophages play a crucial role in immune surveillance and eliminating foreign or cancerous cells from the body. The Macrophage-Mediated Tumor Killing Assay allows researchers to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of macrophages on tumor cells in a controlled and reproducible manner. Creative Bioarray's Macrophage-Mediated Tumor Killing Assay utilizes state-of-the-art techniques and protocols to ensure accurate and reliable results. The assay can be customized to meet the specific needs of each research project, including different types of tumor cells and macrophages.
Reference:
1. Keller R, Keist R, Wechsler A, Leist TP, van der Meide PH. Mechanisms of macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing: a comparative analysis of the roles of reactive nitrogen intermediates and tumor necrosis factor. Int J Cancer. 1990;46(4):682-686. doi:10.1002/ijc.2910460422
Online Inquiry