Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by the progressive loss of motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord. Glutamate excitotoxicity, involving the excessive release and impaired clearance of the neurotransmitter glutamate, is one of the proposed mechanisms contributing to motor neuron death in ALS. The NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor, a subtype of glutamate receptor, plays a significant role in this process.
Creative Bioarray provides this toxic induced ALS cellular models for screening potential drug candidates aimed at evaluating the neuroprotective effect.
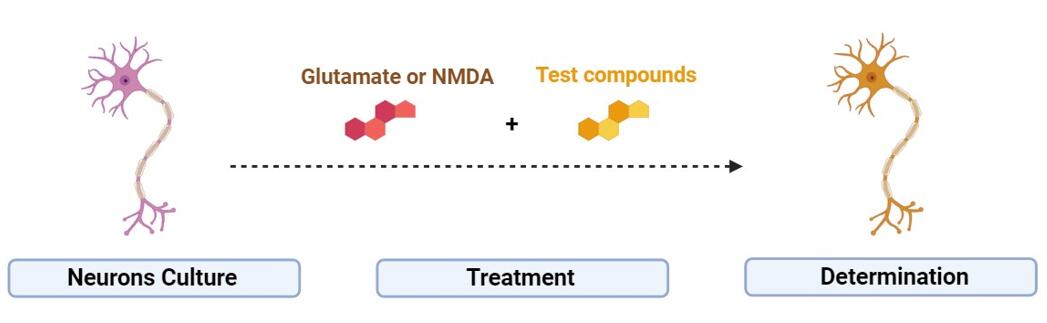 Figure 1. Toxic Induced
Models. Neuron cultures sustain injury from acute intoxication with glutamate or NMDA. The neuroprotective efficacy of compounds is assessed by their
capacity to mitigate this damage.
Figure 1. Toxic Induced
Models. Neuron cultures sustain injury from acute intoxication with glutamate or NMDA. The neuroprotective efficacy of compounds is assessed by their
capacity to mitigate this damage.
Online Inquiry