High-Content Screening (HCS)
HCS is the process of screening large libraries of compounds or genetic manipulations on cells or organisms using automated imaging systems. This allows for the rapid and systematic evaluation of the effects of these compounds or genetic manipulations on various cellular processes. HCS can be used to study a wide range of cellular parameters, such as cell morphology, protein localization, cell proliferation, and cell death.
High-Content Analysis (HCA)
HCA refers to the analysis of the data generated from HCS experiments. It involves the use of advanced image analysis algorithms and statistical techniques to extract quantitative information from the images. This information can then be used to identify hits, classify different cell phenotypes, or study the effects of compounds on specific cellular pathways. HCA allows for the extraction of more detailed and quantitative data compared to traditional manual microscopy techniques.
In summary, HCS is the experimental part of the process that involves automated imaging and data collection, while HCA is the computational and analytical part that involves extracting meaningful information from the acquired data. Together, they form a powerful approach for studying cellular responses in a high-throughput manner, particularly in the context of drug discovery, functional genomics, and other cell biology applications.
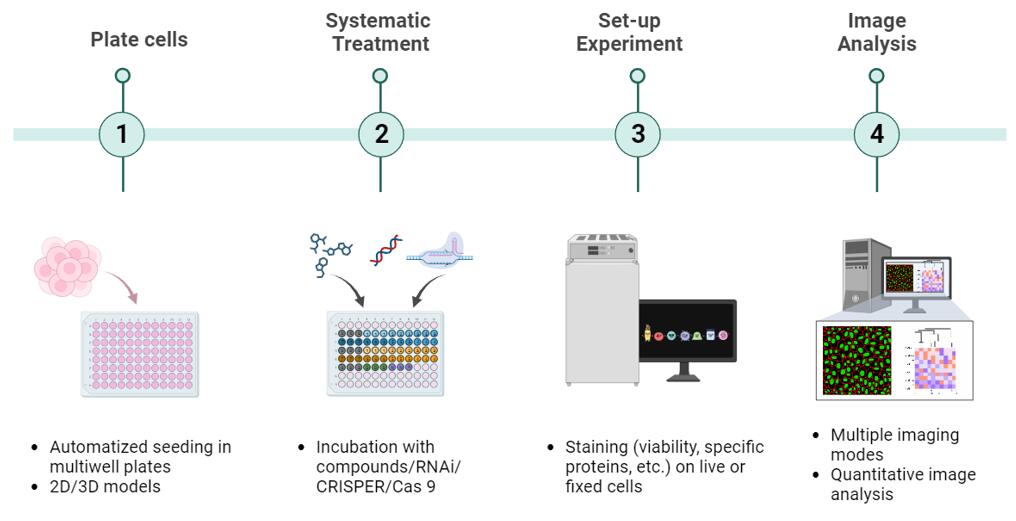
The combination of 2D/3D cell models with HCS & HCA enables researchers to assess the effects of drugs or other compounds in a more biologically relevant context. Creative Bioarray's team of scientists and experts collaborate closely with clients to tailor and refine 2D/3D cell-based high-content screening (HCS) protocols, integrating them with high-content analysis (HCA). This combination empowers researchers to evaluate the impact of drugs or other substances in a biologically meaningful setting. Our comprehensive and top-notch support spans the entirety of the experiment, encompassing study design, execution, and data analysis.
Cell Model Type:
Cell Types Available:
Markers:
Cell Model Type:
Cell Types Available:
Markers:
Cell Model Type:
Cell Types Available:
Markers:
Online Inquiry