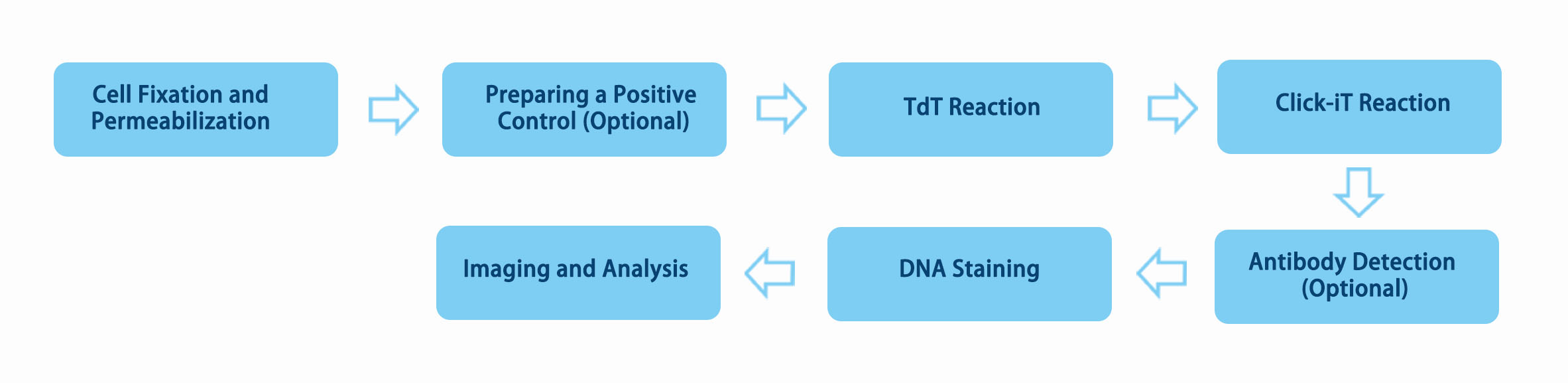
DNA fragmentation is the main biochemical characteristic of cell apoptosis. Chromatin DNA breaks at the junctions between nucleosomeunits, forming large DNA fragments with a length of 50~300kbp, or oligonucleotide fragments with integer multiples of 180~200bp. Creative Bioarray can provide fast, convenient, and accurate TUNEL assay services.
In apoptosis, chromosomal DNA double-strand breaks or single-strand breaks produce a large number of sticky 3'-OH ends. Derivatives formed by deoxyribonucleotides and luciferin, peroxidase, alkaline phosphatase or biotin are labeled to the 3'-end of DNA under the action of deoxyribonucleotide terminal transferase (TdT). Thus, apoptotic cells can be detected. This type of method is called terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL).
We provide an improved TUNEL assay to help customers' research. Our services include but are not limited to:
Traditional TUNEL analysis has many limitations. In the early analysis, dUTP is usually labeled with biotin or fluorescein, and its labeled dUTP has low efficiency in incorporating DNA. It was later improved using Br-dUTP to replace biotin or fluorescein-labeled dUTP. However, Br-dUTP needs to be detected with antibodies, which requires strict reaction conditions.

Creative Bioarray uses dUTP modified with alkyne groups (EdUTP), which is smaller than Br-dUTP and is more easily incorporated into DNA ends by TdT. Through a copper-catalyzed reaction between azide and alkyne (click reaction), the alkyne group is covalently linked to the azide compound, and TUNEL detection is performed with the aid of biotin or fluorescent label on the azide. We provide three kinds of fluorescein (Alexa Fluor 640, Alexa Fluor 488, FITC) labeled TUNEL detection.
Paraffin-embedded tissue sections, frozen tissue sections, cultured cells and cells isolated from tissues.
The time depends on the experiment content
If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more detailed information.
Online Inquiry