Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 are specific forms of amyloid-beta(Aβ) peptides, which are small protein fragments derived from the amyloid precursor protein (APP). These peptides play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease (AD). In AD, there is an accumulation and aggregation of amyloid-beta peptides, leading to the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain.
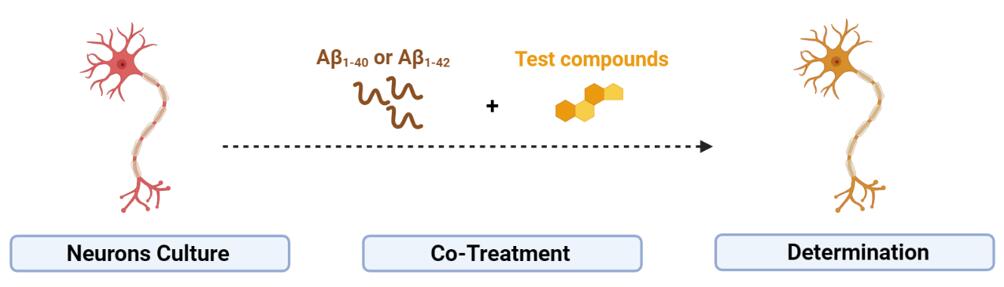
Intoxication of neuronal cultures with Aβ1-40 or Aβ1-42 is a widely employed experimental model in Alzheimer's disease (AD) research. Creative Bioarray provides this toxicity induced cellular models for screening potential drug candidates aimed at mitigating the toxic effects of Aβ and potentially slowing down or preventing the progression of AD.
Online Inquiry